Technical SEO ensures your website is fast, crawlable, and optimized for search engines. Without it, even great content won’t perform. This 10-step checklist covers everything from fixing crawl issues to improving mobile speed and adding local schema markup. Here’s what you’ll learn:
- Run a technical SEO audit to identify crawl errors and indexation issues.
- Optimize Core Web Vitals (LCP, CLS, INP) for mobile users.
- Add local business schema markup to boost visibility in search results.
- Submit an XML sitemap to guide search engines to your key pages.
- Fix duplicate content using canonical tags and redirects.
- Improve page speed by compressing images and optimizing JavaScript.
- Build internal links to help search engines navigate your site.
- Monitor SEO performance regularly to maintain results.
Ready to leave your competitors behind? Start with these actionable steps today.
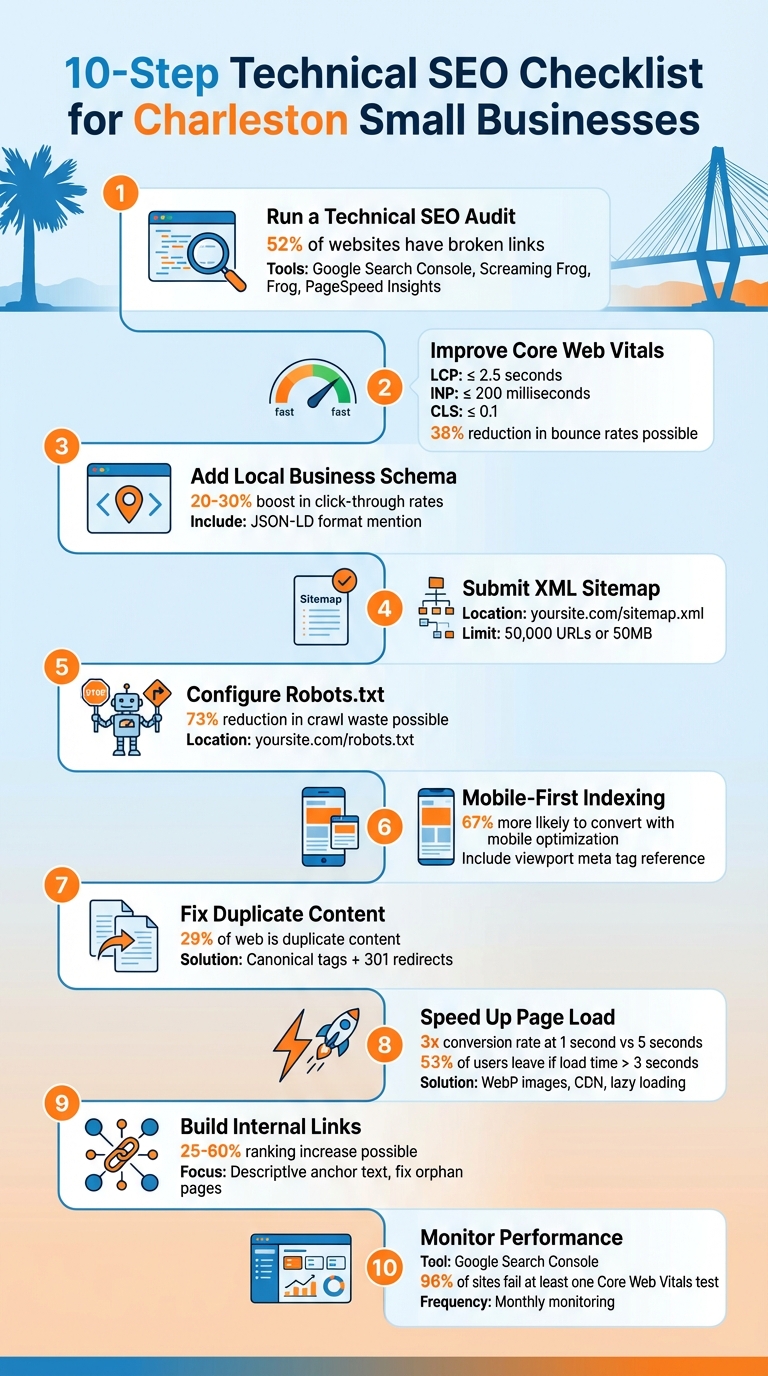
10-Step Technical SEO Checklist for Charleston Small Businesses
Complete Technical SEO Guide 2026 (Fix Crawl, Index & Speed Issues)
Step 1: Run a Complete Technical SEO Audit
A technical SEO audit helps uncover crawl issues, speed bottlenecks, and mobile-related glitches that could be holding your site back. The good news? You don’t need a pricey agency – there are plenty of tools available to pinpoint these problems.
Start with Google Search Console. This free tool lets you see exactly how Google views your site, flagging crawl errors, indexing problems, and even security issues. For example, the "Pages" report can reveal why some pages are excluded from Google’s index. Common reasons include accidental "noindex" tags from plugins or blocks in your robots.txt file. To double-check your indexation, try typing site:yourdomain.com into Google. If the total number of results doesn’t match your actual page count, you’re likely dealing with indexing issues.
For a deeper dive, consider using a crawling tool like Screaming Frog SEO Spider. It mimics Googlebot’s behavior, helping you uncover 404 errors, duplicate content, and redirect chains. When integrated with Google Search Console and Analytics, it provides even more insights, such as identifying orphan pages – URLs that exist but lack any internal links. According to research, 69% of websites have at least one orphan page, which can waste your crawl budget.
Here’s a quick breakdown of useful tools for your audit:
| Tool | Primary Function | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Indexing, crawl errors, security | Direct insights from Google |
| Screaming Frog | Broken links, redirect chains | Comprehensive site crawling |
| PageSpeed Insights | Core Web Vitals, load speed | Performance tuning |
| Siteliner | Duplicate content detection | Content quality checks |
Focus on fixing critical issues first, like 5xx errors or 404s on high-traffic pages, to maintain link authority and optimize your crawl budget. Did you know that 52% of websites have broken internal or external links? Fixing these not only improves user experience but also signals to search engines that your site is well-maintained. Additionally, ensure that every key page is accessible within three clicks from your homepage – pages buried deeper than four clicks often get ignored by search engines.
Step 2: Improve Core Web Vitals for Mobile and Local Searches
Core Web Vitals measure how users experience your website in terms of speed, responsiveness, and visual stability. These metrics – Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), and Interaction to Next Paint (INP) – play a direct role in search rankings. This is especially true for mobile and local searches, where Charleston customers frequently look for businesses "near me".
The stakes are high. A slow mobile experience can drive potential customers away before your page even finishes loading. Take this example: In January 2026, a neighborhood café in Charleston worked on improving its mobile Core Web Vitals by compressing images, deferring non-essential JavaScript, and setting explicit size attributes for embedded content. Their efforts brought LCP down from 4.2 seconds to 2.0 seconds. The result? A 38% reduction in mobile bounce rates and a 22% boost in click-to-call actions and walk-in visits.
| Metric | Good Threshold | What It Measures |
|---|---|---|
| LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) | ≤ 2.5 seconds | How quickly the main content appears |
| INP (Interaction to Next Paint) | ≤ 200 milliseconds | How quickly your site reacts to user inputs |
| CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) | ≤ 0.1 | How stable your page layout is during loading |
Here’s how you can improve mobile performance and enhance your local search visibility.
Speed Up Mobile Page Load Times
Start with images – they’re often the biggest culprits behind slow load times. Convert them to modern formats like WebP, which are around 34% smaller than JPEGs or PNGs. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to serve content from servers closer to your Charleston audience, cutting down server response times. Aim for a Time to First Byte (TTFB) under 200 milliseconds.
To prioritize loading of your LCP image, add fetchpriority="high" in the HTML. Always define width and height attributes for images and videos – unsized media can cause layout shifts, which hurt your CLS score. In fact, 66% of web pages have at least one unsized image. If your site relies heavily on JavaScript, use the scheduler.yield() API to break tasks into chunks under 50 milliseconds, keeping the site responsive.
These optimizations won’t just improve Core Web Vitals; they’ll also make your site more appealing to mobile users, boosting your local search rankings.
Optimize for Local Search Patterns
For local SEO, mobile performance is key. Most "near me" searches happen on smartphones, making it critical for Charleston users to find your business quickly and easily. Websites that load faster tend to rank higher in the Local Pack, which directly drives phone calls and foot traffic.
Make sure your business Name, Address, and Phone number (NAP) are in crawlable HTML text instead of being embedded in images – search engines can’t read text inside images. Adjust button and link sizes to prevent accidental clicks, ensuring touch targets are large and spaced out. To avoid layout shifts while custom fonts load, use font-display: swap in your CSS.
Step 3: Add Local Business Schema Markup
Schema markup helps search engines identify your Charleston location, supporting your Google Business Profile and enabling rich search results like star ratings, price ranges, and photos. Even if your page lacks specific keywords, schema markup ensures Google connects your business to searches such as "Charleston bakery" or "attorney near me".
This structured data benefits not just traditional search but also AI-driven platforms like ChatGPT and Google’s AI Mode. Pages with schema markup are more likely to be included in AI-generated summaries. As Alex Lindley, Managing Editor at Semrush, explains:
"Local business schema makes it easier for search engines to understand and highlight your business."
How to Add LocalBusiness Schema
The simplest way to add schema is by using the JSON-LD format, which Google prefers because it doesn’t slow down page load times. If you’re on WordPress, plugins like Yoast Local SEO, Rank Math, or Schema Pro make it easy to include the necessary details without coding. For those comfortable with HTML, you can manually add JSON-LD directly to your site.
Start with essential information: your business name, full address, primary phone number, and operating hours. Include latitude and longitude using the geo property and add sameAs links to your social media profiles. If your business serves customers at their locations – like a plumber or landscaper – use the serviceArea property to specify the Charleston neighborhoods or regions you cover.
Whenever possible, avoid the generic LocalBusiness tag. Instead, choose a more specific subtype such as Restaurant, MedicalClinic, or Attorney. This helps search engines better categorize your business. For step-by-step instructions, check out how to add local business schema markup.
| Business Type | Recommended Schema Properties | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Restaurant | servesCuisine, menu, acceptsReservations |
Highlights food type and booking options |
| Medical Practice | medicalSpecialty, isAcceptingNewPatients |
Helps patients find specific care |
| Law Firm | serviceType, areaServed |
Specifies legal expertise and geographic reach |
| Service Business | serviceArea, priceRange |
Shows where you operate and relative cost |
How Local Schema Helps Charleston Businesses
Adding schema markup increases the likelihood of appearing in Google’s Local Pack – the top three business listings often displayed with a map. Businesses featuring rich results in local search typically experience a 20–30% boost in click-through rates compared to standard listings. This translates to more calls, direction requests, and customers visiting your location.
With zero-click searches on the rise, accurate schema becomes even more critical. Features like AI Overviews and enhanced Local Packs allow users to see essential details – like your hours, phone number, and services – without needing to visit your website. As Sebastian Żarnowski, Co-founder & CEO of Localo, explains:
"The more specific you get, the better Google understands exactly the services you offer. This increases your chances of appearing in relevant local searches."
For Charleston businesses competing in a busy market, schema markup is no longer optional. It’s a key element of local search visibility. When combined with strong Core Web Vitals and a mobile-friendly site, it sets the stage for dominating local search results. Up next: ensure your site is fully crawlable and indexed by submitting an XML sitemap to Google Search Console.
Step 4: Submit an XML Sitemap to Google Search Console
An XML sitemap is essentially a roadmap for search engines, listing the URLs you want them to index. It helps Google find your most critical pages – like service pages or Charleston neighborhood landing pages – that might not be easily accessible through your site’s regular navigation. While submitting a sitemap doesn’t guarantee every page will be crawled, it can make the process more efficient and help Google focus on your local content.
Most content management systems (CMS) like WordPress (with Yoast SEO), Wix, and Squarespace automatically generate sitemaps. Your sitemap should be located at your site’s root directory, such as charlestonbusiness.com/sitemap.xml. Make sure it only includes pages with a 200 status code and that are self-canonical. Exclude utility pages like login screens or "thank you" pages. Instead, emphasize service-area pages, location-specific landing pages, and hyper-local blog content targeting areas like Mount Pleasant or West Ashley.
Once your sitemap is ready, submit it via Google Search Console. To do this, go to the Sitemaps report under the Indexing section, enter your sitemap’s URL (e.g., sitemap.xml), and click "Submit." If Google processes it successfully, you’ll see a "Success" status, along with details like the number of discovered pages and the last time the file was read. For broader accessibility, add a Sitemap directive to your robots.txt file (e.g., Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml) so other search engines can locate it as well.
Before finalizing, use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console to check for errors, such as 404s or 301 redirects, which could waste your crawl budget. Including the <lastmod> tag in your sitemap is another good practice – it tells Google when a page was last updated, helping it prioritize fresher content. Keep in mind that a single sitemap is capped at 50,000 URLs or 50MB when uncompressed.
After submitting and validating your sitemap, Google will begin crawling your key pages more efficiently. From here, you can move on to configuring your robots.txt file to further enhance crawl efficiency in Step 5.
Step 5: Configure Robots.txt for Better Crawl Efficiency
The robots.txt file plays a key role in guiding search engine bots, telling them which parts of your website to crawl and which to skip. When set up effectively, it ensures bots focus on your high-priority pages – like service pages or neighborhood-specific landing pages – instead of wasting time on admin sections or duplicate content. As SC SEO Experts explains:
"Crawling is the process by which Google discovers new and updated web pages. It’s important because your site needs to be crawled to be indexed and ranked."
To get started, place your robots.txt file in the root directory of your site (e.g., charlestonbusiness.com/robots.txt) and use simple directives. The User-agent directive specifies the bot you’re targeting (use User-agent: * to address all bots). The Disallow directive blocks specific paths. For instance, Disallow: /wp-admin/ stops bots from accessing your WordPress backend, while Disallow: /*?s=* prevents indexing of internal search result pages, which often create duplicate content. Don’t forget to include your sitemap URL in the file to guide bots to your key pages:
Sitemap: https://charlestonbusiness.com/sitemap.xml.
Common Robots.txt Pitfalls to Avoid
Misconfigurations in robots.txt can hurt your site’s visibility. For example, never block CSS, JavaScript, or image files—a key step in mobile SEO audits – Google needs these to render your pages correctly. Also, be mindful of case sensitivity in path names. For example, /wp-admin/ works, but /Admin/ will not.
A real-world example highlights the impact of proper configuration: In early 2026, an e-commerce site reduced crawl waste by 73% in just 90 days by blocking unnecessary filter URLs. This change sped up new product indexing from 21 days to just 4 and increased organic traffic by 58%.
Testing and Fine-Tuning Robots.txt
Before deploying changes, always test your robots.txt file in Google Search Console. A common error – like accidentally pushing a staging site’s Disallow: / directive to production – could make your entire site invisible to search engines overnight. Keep in mind, though, that robots.txt prevents crawling, not indexing.
For small businesses in Charleston, focus on blocking low-value pages such as /cart/, /checkout/, and /thank-you/. Also, consider blocking URL parameters that generate duplicate content. Direct bots toward your essential pages, such as service offerings, location-specific content for areas like Mount Pleasant or James Island, and blog posts optimized for local keywords. These tweaks ensure search engines prioritize the content most relevant to Charleston users.
For more advanced tips on configuring robots.txt, check out SearchX’s ultimate guide to robots.txt for SEO.
Step 6: Ensure Mobile-First Indexing and Responsive Design
If you’re a small business in Charleston looking to get ahead of the competition, mobile-first indexing is a must. Google now prioritizes the mobile version of your website when it comes to indexing and ranking. As Carlos Silva from Semrush puts it:
"Mobile-first indexing means Google’s web crawler prioritizes indexing the mobile version of a website’s content over its desktop counterpart".
This shift is especially relevant for Charleston businesses. With nearly one-third of mobile searches being location-based, potential customers looking for services like "plumber near Mount Pleasant" or "best brunch in downtown Charleston" are likely searching from their phones. If your mobile site is slow or poorly designed, you could lose these customers before they even get a chance to explore your offerings. In fact, businesses with mobile-optimized websites are 67% more likely to convert visitors into customers. Your mobile site’s performance is directly linked to how Google ranks you and how easily Charleston locals can find you.
To make sure your mobile site is up to par, you’ll need to test its usability and performance.
Test Mobile Usability
Use tools like PageSpeed Insights to evaluate your mobile site’s performance and check Core Web Vitals. Simply enter your website’s URL, and you’ll get a detailed report about your mobile performance. Focus on these key metrics:
| Metric | Focus Area | Goal for Mobile |
|---|---|---|
| LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) | Loading Speed | Under 2.5 seconds |
| INP (Interaction to Next Paint) | Responsiveness | Under 200 milliseconds |
| CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) | Visual Stability | Under 0.1 |
Additionally, use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console to see how Googlebot views your mobile pages. Pay attention to any blocked resources, such as CSS, JavaScript, or images, that could prevent your site from rendering correctly. Also, check for touch target issues – interactive elements like buttons should be at least 48×48 CSS pixels with a minimum of 8 pixels of spacing between them. This ensures users can easily tap without accidental clicks.
Once you’ve tested your site, it’s time to implement design practices that make it more mobile-friendly.
Responsive Design Best Practices
Google Search Central strongly recommends using responsive web design because:
"it’s the easiest design pattern to implement and maintain".
Start by including the meta viewport tag in your site’s HTML:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> This tag ensures your site adapts to the screen size, rather than forcing a desktop layout onto mobile devices. Use fluid layouts with percentages and CSS tools like Flexbox or Grid instead of fixed widths. For readability, set a base font size of at least 16px for body text.
Optimize your images by using the srcset and sizes attributes, so your site serves the right image size for each device. For instance, someone browsing on their iPhone in King Street doesn’t need a massive 4000px header image.
Ensure your mobile site mirrors your desktop version. This means keeping headings, metadata, structured data, and service descriptions consistent. Avoid hiding key content in tabs or accordions unless it’s still crawlable by search engines. Display your Name, Address, and Phone number (NAP) in plain HTML text, not as part of an image. Finally, steer clear of intrusive pop-ups that could frustrate users on smaller screens.
Step 7: Fix Duplicate Content and Use Canonical Tags
Once your site is mobile-friendly, it’s time to tackle duplicate content – a common issue that can weaken your SEO efforts.
Duplicate content can hurt Charleston small businesses by splitting SEO strength across multiple pages. For example, having separate service pages for areas like Mount Pleasant, James Island, and West Ashley with nearly identical content can dilute your ranking potential. Google describes duplicate content as "substantive blocks of content within or across domains that either completely match other content or are appreciably similar". Essentially, instead of boosting your rankings, these pages end up competing with each other, leaving you at a disadvantage against other local businesses.
Here’s a surprising stat: about 29% of the web is duplicate content. When your site contributes to this, search engines may struggle to determine which page to rank. As Chima Mmeje from Moz puts it:
"Extensive duplication can dilute your website’s ranking capability across cannibalized pages rather than consolidating it into one authoritative page".
This is especially harmful in Charleston’s competitive local market, where 91% of organic traffic goes to first-page search results.
How to Fix Duplicate Content
1. Use Canonical Tags
Canonical tags signal to search engines which version of a page is the "master" copy. Add this tag to the <head> section of duplicate or similar pages, using the full URL with https://:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://yoursite.com/preferred-page" /> For pages that you want to rank individually, include a self-referencing canonical tag.
2. Redirect Old or Duplicate Pages
If you’re consolidating content, use a 301 redirect to permanently send users and search engines to your preferred URL. This also preserves any link equity from the old page.
3. Exclude Unnecessary Pages from Search
For pages like printer-friendly versions that users need but shouldn’t appear in search results, use a noindex, follow meta tag.
4. Audit Your XML Sitemap
Make sure your sitemap only includes canonical URLs, not duplicate ones.
Expert Advice for Local Businesses
Local SEO expert Miriam Ellis from Moz offers a practical tip:
"It’s better to go with just a strong page for each city and a strong page for each service, rather than creating lots of thin or duplicate city/keyword combo pages".
For Charleston businesses, this might mean creating a single, detailed "HVAC Repair in Charleston" page with sections for neighborhoods like Mount Pleasant or West Ashley, rather than spreading your content across multiple weaker pages that compete with each other.
Once your duplicate content is managed, you’ll be ready to focus on building an effective internal linking structure in the next step.
Step 8: Speed Up Page Load Times
Page speed is a game-changer – it can literally determine whether a visitor becomes a customer or clicks away. A site that loads in just 1 second converts at nearly 3x the rate of one that takes 5 seconds. For Charleston small businesses, where local competition is fierce, this difference can make or break customer acquisition.
Here’s a telling stat: 53% of mobile users will leave a site if it takes more than 3 seconds to load. Since images often make up a large chunk of a webpage’s weight, optimizing them is non-negotiable. Faster load times not only help with SEO but can also directly increase conversion rates for local businesses.
Reduce Main Thread Work
The main thread of a browser handles critical tasks like rendering and script execution. If these tasks take too long, your site can freeze, frustrating users who are trying to scroll, click, or interact with content. Breaking up "long tasks" (those that exceed 50 milliseconds) can prevent these hiccups and keep your site responsive.
A tool like the scheduler.yield() API can help by breaking up lengthy JavaScript tasks, ensuring smoother performance. Additionally, keeping your DOM size smaller speeds up layout recalculations. For example, if you run a Charleston restaurant, this means your online menu or pricing page will load quickly and respond seamlessly, even on mobile devices.
But it’s not just about scripts – your visual content needs attention too.
Optimize Images for Faster Loading
Images are often the largest elements on a page, with 73% of mobile pages using an image as their Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) element. To speed things up, switch to modern formats like WebP, which are 25–35% smaller than traditional JPEG or PNG files. For hero images or key visuals, the AVIF format is an even better option, reducing file sizes by as much as 50% compared to JPEG.
Use tools like TinyPNG or ShortPixel to compress images without sacrificing quality. A good rule of thumb is to keep hero images under 150KB. Pair this with a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to serve images more efficiently – reducing load times by up to 60%. Services like BunnyCDN are affordable, with plans starting as low as $3.45 per month for sites with up to 60,000 monthly visitors.
For additional speed boosts, use loading="lazy" on offscreen images. This simple tweak can improve initial load times by 25% to 40% on image-heavy pages. Don’t forget to set explicit width and height attributes on images – this helps minimize Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), avoiding those annoying jumps when images load.
Finally, a branded CDN URL not only speeds up delivery but also supports better indexing by search engines. Once your page speed is optimized, you’ll be ready to tackle internal linking, which further enhances user experience and SEO.
Step 9: Build a Clear Internal Linking Structure
Internal links play a big role in helping search engines find your pages, understand your site’s hierarchy, and spread authority across your site. Done right, internal linking can increase rankings by 25–60% and boost the number of indexed pages by up to 30%. That’s a serious advantage when trying to stand out to local customers searching for your services.
Start by linking your homepage to your main service pages, then connect those service pages to Charleston-specific landing pages. This creates a clear structure that shows Google what you offer and where you operate. It also ties into earlier efforts like improving crawl efficiency and speeding up your site by making navigation easier for search engines. If your business has five or fewer locations, link directly to them from your main navigation or a "Store Locations" tab. Use descriptive anchor text like "Charleston HVAC repair services" instead of vague phrases like "click here." Descriptive text not only helps search engines understand the link’s purpose but also ensures links are easy to tap on mobile devices.
Next, check for orphan pages (pages with no incoming links) and dead-end pages (pages with no outgoing links). Tools like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console can help you find these problem areas. Orphan pages are essentially invisible to search engines, while dead-end pages trap link equity and stop crawlers from moving through your site. Fixing these issues ensures that your most important content – like service pages or customer testimonials – gets the attention it needs.
Make sure your internal links are in crawlable HTML text, not hidden in images. This is especially critical for your business name, address, and phone number (NAP), which should be easy for both users and search engines to access.
Finally, avoid creating "doorway pages." Each Charleston-specific landing page should feature unique, high-quality content. Include elements like local projects, community involvement, or customer stories from the area. This approach not only improves your SEO but also builds trust with local customers by showing you’re genuinely connected to the Charleston community.
With your internal links now optimized to guide crawlers and distribute authority effectively, you’re ready to move on to Step 10 and focus on monitoring and maintaining your SEO performance.
Step 10: Monitor and Maintain SEO Performance
Technical SEO isn’t a "set it and forget it" kind of task – it requires consistent attention to keep your Charleston business performing well in search rankings. Even after completing the earlier steps, your site may encounter new issues due to updates or content changes. That’s why it’s crucial to monitor your SEO performance regularly – ideally, on a monthly basis – to catch potential problems before they impact your rankings.
A key tool for this is Google Search Console, which is both powerful and free. Start by reviewing the Pages report to check which pages Google has successfully indexed and which it hasn’t. Keep an eye out for warnings like "Crawled – currently not indexed", as these could prevent important service pages from showing up in search results. Use the URL Inspection Tool to test individual pages and ensure they’re being crawled and indexed correctly. Additionally, the Core Web Vitals report should be checked monthly to track metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), Interaction to Next Paint (INP), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). These metrics are critical, especially since 96% of websites fail at least one Core Web Vitals test. Regular monitoring of these areas ensures your earlier technical optimizations remain effective.
Beyond indexing, focus on your Search Performance metrics – clicks, impressions, click-through rate (CTR), and average position. These metrics help validate the improvements you’ve made in steps 1 through 9. Export query data and look for terms like "near me" or "[service] in Charleston" to uncover customer search trends and inspire new content ideas. As Akmal Faizan, Founder of Stech Local, explains:
"Most businesses track what happens after a click – but GSC tells you what caused the click in the first place. That’s where local growth actually starts".
This kind of feedback loop strengthens the technical SEO foundation you’ve built.
Don’t overlook the Manual Actions report either. If your site violates Google’s spam policies, it could be removed from search results entirely. Be vigilant about addressing 5xx server errors, robots.txt blocks, and security issues that could flag your site as unsafe. If your business operates multiple locations in Charleston, submitting a dedicated XML sitemap (e.g., sitemap-locations.xml) can help Google discover and index these pages more efficiently. For deeper insights, connect Google Analytics 4 with Search Console to view search queries alongside on-site behavior and conversions in one streamlined dashboard.
Conclusion: Dominate Charleston Search Results with Technical SEO
With the steps outlined above, you’re ready to elevate your website’s performance and visibility. This technical SEO roadmap is tailored to help Charleston businesses address the common challenges that hinder local search rankings. From conducting thorough audits and improving Core Web Vitals and fixing common issues to adding local schema markup and keeping a close eye on performance metrics, these strategies lay the groundwork for better crawlability and stronger local visibility.
Technical SEO plays a critical role – it’s what ensures your Charleston business appears when potential customers search for your services. As Eugen Platon, Technical SEO Specialist at onwardSEO, aptly says:
"The technical foundation you build today determines your visibility tomorrow."
With search engines increasingly leaning on AI-driven results and conversational tools, having a well-structured, machine-readable site is more crucial than ever.
While implementing these strategies requires time and effort, the payoff is clear. Expect faster load times, smoother mobile experiences, better indexation, and improved rankings for "near me" searches. Whether you choose to handle these tasks on your own or bring in professional help, the key is to take action now – your competitors are already working on it.
For those looking to fast-track their growth, SearchX offers technical SEO services that can manage the heavy lifting. Starting at $6,000/month, the Growth plan includes detailed audits, 6-8 pieces of content, and ongoing conversion tracking optimization – everything your business needs to dominate Charleston’s search landscape. Prefer a hands-on approach? Check out our DIY local SEO resources for expert-driven guidance.
FAQs
Which technical SEO fixes should I do first?
Start by addressing the basics that allow search engines to effectively navigate and understand your site. Check your robots.txt file to ensure it’s not accidentally blocking important pages. Next, fix any broken links to enhance user experience and maintain link equity. Don’t forget to update your XML sitemap so search engines have an accurate roadmap of your site.
Since many local searches happen on mobile devices, optimize your site’s mobile speed and responsiveness to meet user expectations. Lastly, add LocalBusiness schema markup to help search engines grasp key details about your business and boost your visibility in local search results.
How long until technical SEO improves my rankings?
Rankings from technical SEO efforts usually begin to improve within 1 to 3 months if you’re consistent. However, for more noticeable, long-term gains, it often takes 6 to 12 months. The key? Stay consistent and patient – SEO is a marathon, not a sprint.
What local schema fields matter most for Charleston SEO?
For Charleston SEO, it’s essential to use LocalBusiness schema markup that includes precise name, address, and phone number (NAP) details. Consistency across all platforms is critical for accuracy. To strengthen your local presence, include geo-coordinates, business categories, opening hours, and even images that showcase well-known Charleston landmarks or neighborhoods. Adding specific local details, such as references to areas like Mount Pleasant or King Street, enhances your visibility in local searches. This helps search engines provide more relevant results for services based in Charleston.
Related Blog Posts
- Is Your Charleston Website Ready for Local SEO? Use This 10-Point Checklist
- How This Charleston Event Rental Company Ranked #1 in Just 6 Months
- Local SEO South Carolina Checklist: 10 Steps to Higher Rankings
- Charleston SC SEO in 2025: Why 47% of Local Businesses Are Switching Strategies (And You Should Too)




